Paolo Buono
Assistant Professor
PhD in Computer Science
phone: +39 080 544 2239
email: paolo.buono@uniba.it
room: 517 (5th floor)
office hours: Thursday 11.00-13.00
Paolo Buono
Research
Interests:
Human-Computer Interaction, Information Visualization, Visual Analytics,
Mobile Computing, IoT, Video analysis, Web-based Systems, Time Series
Interaction
Curriculum
Paolo Buono is assistant professor at the Computer Science
Department of the University of Bari.
He currently teaches Software Development for Mobile Devices (Bachelor degree), Information Visualization (Master degree, in English), Security in Mobile Environments (Master degree).
He holds a PhD in Computer Science on the subject of Visual Data Analysis.
His current research interests include Visual Analytics,
Information Visualization, Human-Computer Interaction, Mobile
Applications, Dynamic hypergraph visualization.
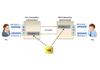
He was co-founder and CEO of LARE, a spin off of the University of Bari
aiming at providing real-time remote support to surgeons during
surgeries, through audio-video connection and telestration.
Since 2002 he is a member of the METEA
Research Center, a multidisciplinary center performing activities
related to environment protection. At METEA, he is the computer science
expert coordinating several research and development activities.
In the periods August-September 2019, January-February 2017, and June-July 2017 he has been
visiting scientist at AVIZ research team
at INRIA (France), carrying out research on Information Visualization.
In 2010 he was invited to the Dagstuhl Seminar 10241 on "Information Visualization".
In the period 2004-2005 he has been visiting scientist at Human-Computer Interaction Lab of the University of Maryland (USA), primarily working on Time Series Visualization.
In the period 2001-2003 he has been visiting scientist for several short periods at Fraunhofer IPSI at Darmstadt (Germany).
He is or has been involved in the scientific organization of several conferences:
General co-chair of the 18th IFIP TC.13 International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (INTERACT 2021)
Program co-chair of the International Conference on Advanced Visual
Interfaces (AVI
2016)
Publicity co-chair for the international symposium
IS-EUD 2011
Poster chair of the AVI 2010 International Conference
Co-chair of the Human Machine Interaction track of the HSI '09 and HSI '10 conference
Co-chair in the Organizational Overview track of INTERACT 2005 Conference
Volume editor of the Adjunct Proceedings of INTERACT 2005 Conference
Scientific secretariat of the AVI 2004 Conference
Co-organizer of the WUAV 2013 - 1st International Workshop on User-Adaptive Visualization workshop
He is regularly in the PC of HCI conferences and particularly in the PC
of conferences in the area of Information Visualization and Visual
Analytics, including the top conferences of the VIS series.
At the IVU Lab, Paolo Buono coordinates the research on Information Visualization and Visual Analytics. He as been the principal researcher of the University of Bari that has participated to the VisMaster Coordination Action project (2008-2010), sponsored by EU. VisMaster involved the European researchers most active in Visual Analytics.
He has been involved in other projects sponsored by European Union and Italian organizations, in particular:
2000-2001 he has been the responsible of research and development of the visual data analysis component of the FAIRWIS (trade FAIR Web-based Information Services, IST-1999-12641) project.
2002-2004 he has been project manager of the DAE (Data Analysis Engine)
component of the system developed in the FAIRSNET (On-line Solutions for
Trade Fairs, IST-2001-34290) project.
2005-2007 he has been responsible of a research line of a project funded
by the Apulian Region within a program for environment protection. The
output of this research line has been the development of the CET system, i.e. the Land Emissions Cadastre still in use in the Apulia Region.
2007-2009 he has been involved in the project DIPIS, related to the
traceability of products and their transformation in the supply-chain.
2008-2009 he has worked in other several projects: Genómena, MONICA,
CHAT, GeCo.
2014-2015 he has been scientific responsible of the UNIBA unit of the
project LOGIN, funded by the Ministry of Industry and Economical
Development, aimed at developing a digital business ecosystem of
state-of-the art services for logistics.
Paolo Buono is one of the inventors of the patent n. 1401512 that
concerns a multimedia framework and a method to support the visit of a
site of interest, such as an archaeological or a natural park.
He is member of ACM (Association of
Computing Machinery), ACM SIGCHI, and SIGCHI
Italy, the Italian Chapter of ACM SIGCHI.
He speaks Italian, English and French
Top of this page
Publications
This icon  allow
visitors who click on it to obtain the definitive version of the article
from the ACM Digital Library at no charge. Please make sure that the
address of this page visualized in your browser is: http://ivu.di.uniba.it/people/buono.htm
allow
visitors who click on it to obtain the definitive version of the article
from the ACM Digital Library at no charge. Please make sure that the
address of this page visualized in your browser is: http://ivu.di.uniba.it/people/buono.htm
2019
P. Buono, A. Legretto, E. Bertini, M. F. Costabile
Visual techniques to compare predictive models
In Biannual Conference of the Italian SIGCHI Chapter (CHItaly’19), September 23–25, 2019,Padova, Italy.ACM, New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1145/3351995.3352035
Abstract
Predictive analysis is an important part of data analysis. Predictivemodels, based on Statistics or Machine Learning, are increasinglyused to estimate, with a certain probability, future values of thevariables that describe a phenomenon. Different models producedifferent results on a same dataset; thus, several models should becompared in order to identify the most suitable one. The paper ispart of a larger research that aims at providing interactive visual-izations that help the analysts to compare predictive models andto select the model that best fits the data. Specifically, two visual-izations are presented, which support the analysts in performingsome tasks of the Keim’s Visual Analytics Mantra.
P. Buono, G. Desolda, R. Lanzilotti, M. F. Costabile, A. Piccinno
Visualizations of User’s Paths to Discover Usability Problems
In: Lamas D., Loizides F., Nacke L., Petrie H., Winckler M., Zaphiris P. (eds) Human-Computer Interaction – INTERACT 2019. INTERACT 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11749. Springer, Cham. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-29390-1_64
Abstract -
www
This paper reports on an on-going work that investigates the use of visualization techniques to help evaluators discovering usability problems by visualizing data collected during usability tests of web sites. Two visualization techniques are described and some results of the evaluation study that compared the two techniques are provided.
P. Buono, F. Cassano, A. Piccinno, M. F. Costabile
Smart Objects for Speech Therapies at Home
In: Lamas D., Loizides F., Nacke L., Petrie H., Winckler M., Zaphiris P. (eds) Human-Computer Interaction – INTERACT 2019. INTERACT 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11749. Springer, Cham. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-29390-1_60
Abstract -
www
The pervasiveness of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is commonly used to create domestic ambient to support people daily life. In this paper we explore how IoT devices can be used in the smart home to administer the therapy to children with speech disorders. The speech therapist manages and controls patients’ therapies by using End-User Development methods and tools.
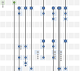
P. Valdivia,
P. Buono, C. Plaisant, N. Dufournaud, J.D. Fekete
Analyzing Dynamic Hypergraphs with Parallel
Aggregated Ordered Hypergraph Visualization
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. In press. DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2019.2933196.
Abstract -
pdf -
bib -
www
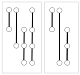
Parallel Aggregated Ordered Hypergraph (PAOH) is a novel technique to visualize dynamic hypergraphs. Hypergraphs are a generalization of graphs where edges can connect several vertices. Hypergraphs can be used to model networks of business partners or co-authorship networks with multiple authors per article. A dynamic hypergraph evolves over discrete time slots. PAOH represents vertices as parallel horizontal bars and hyperedges as vertical lines, using dots to depict the connections to one or more vertices. We describe a prototype implementation of Parallel Aggregated Ordered Hypergraph, report on a usability study with 9 participants analyzing publication data, and summarize the improvements made. Two case studies and several examples are provided. We believe that PAOH is the first technique to provide a highly readable representation of dynamic hypergraphs. It is easy to learn and well suited for medium size dynamic hypergraphs (50-500 vertices) such as those commonly generated by digital humanities projects—our driving application domain.
@article{valdivia:hal-02264960,
TITLE = {{Analyzing Dynamic Hypergraphs with Parallel Aggregated Ordered Hypergraph Visualization}},
AUTHOR = {Valdivia, Paola R and Buono, Paolo and Plaisant, Catherine and Dufournaud, Nicole and Fekete, Jean-Daniel},
URL = {https://hal.inria.fr/hal-02264960},
JOURNAL = {{IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics}},
PUBLISHER = {{Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers}},
YEAR = {2020},
DOI = {10.1109/TVCG.2019.2933196},
KEYWORDS = {interaction ; usability ; digital humanities ; case study ; dynamic hypergraph ; Index Terms-dynamic graph},
PDF = {https://hal.inria.fr/hal-02264960/file/Paohvis.pdf},
HAL_ID = {hal-02264960},
HAL_VERSION = {v1},
}

P. Buono, F. Balducci, F. Cassano, A. Piccinno
EnergyAware: A Non-intrusive Load Monitoring System to Improve the Domestic Energy Consumption Awareness
In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGSOFT International Workshopon Ensemble-Based Software Engineering for Modern Computing Platforms (EnSEmble’19), August26, 2019, Tallinn, Estonia. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3340436.3342726.
Abstract
The correct use of energy can heavily impact on a family monthly bills and can also contribute to reduce the global air pollution production. Despite many available systems for domestic energy consumption, the real understanding of how domestic devices affect the total energy consumption is still a challenge. The Internet of Things (IoT) technology may contribute to the improvement of the energy habits awareness, by connecting sensors and mobile devices to provide people real-time consumption of a domestic environment. Many attempts have been done to integrate environmental sensors, mobile devices and people but this remains a challenge. This paper presents the use of a cheap and easy to apply Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) system that show people their historical and real-time domestic energy consumption on mobile devices and sends them alerts if an energy overload is about to occur.

P. Buono, P. Carella
Towards secure mobile learning. Visual
discovery of malware patterns in android apps
In 23 International Conference Information Visualisation.
pp. 364-369. 02-05 July 2019. ISBN:978-1-7281-2838-2.
Abstract
Due to the diffusion of mobile devices, more and more
people access e-learning platforms from mobile phones. Students learn
from digital books and have access to information anytime and
anywhere. However, with billions of mobile users worldwide, as well as
billions of under-protected Internet of Things (IoT) devices, the risk
of being the target of malware, cybercrime and sophisticated attacks
is high.This paper proposes and discusses a set of visualization
techniques applied to a dataset generated by DREBIN, a malware
detection tool that performs a
staticanalysisonappsinstalledtoAndroiddevices.Onthebaseof dataset, we
applied text, tree and graph visualization techniques to identify
malware patterns. The visual ?ndings can help the cybersecurity
analyst in detecting malicious app behavior.
P. Buono, C. Cassano, A.
Piccinno, T. Roselli, V. Rossano, F. Berni
Multimedia technologies to support delivery of
health services to migrants by enhancing their inclusion
In 23 International Conference Information Visualisation. pp. 370-375. 02-05 July 2019. ISBN:978-1-7281-2838-2. DOI: 10.1109/IV.2019.00069
Abstract -
bib -
www
Due to its geographical position, the Apulia region, is used to house migrants from all over the world who arrived over the centuries. Apulia is also a transit land for migrants that want to reach other Italian regions or European countries. One of the main issues of migration flows is related to the health services network. In this context, the Apulia Region, in collaboration with other private and public organisations, proposed the Prevenzione 4.0 (Prevention) project that aims at creating an e-health environment to empower the services of the National Health Service for migrants. Technological solutions and learning paths will be implemented to reduce the number of users who daily ask for health care services. The actions will be available for both migrants and professional figures involved in the management of migrants’ reception processes. This paper presents a mobile application designed to help the migrant centres to provide medical and psychological support to their guests. The app fosters the migrants’ empowerment to make them able to take care of their health without involving the National Health Service when not strictly necessary.
@INPROCEEDINGS{8812103,
author={P. {Buono} and F. {Cassano} and A. {Piccinno} and V. {Rossano} and T. {Roselli} and F. {Berni}},
booktitle={2019 23rd International Conference Information Visualisation (IV)},
title={Multimedia Technologies to Support Delivery of Health Services to Migrants by Enhancing their Inclusion},
year={2019},
volume={},
number={},
pages={370-375},
keywords={Medical services;Monitoring;Computer science;Biomedical monitoring;Psychology;Cultural differences;Collaboration;e-health;mobile devices;microlearning;customisation},
doi={10.1109/IV.2019.00069},
ISSN={2375-0138},
month={July}
}
D. Malerba, A. Appice,
P. Buono, G.
Castellano, B. De Carolis, M. de Gemmis, M. Polignano, V. Rossano, L. M.
Rudd
Advanced Programming of Intelligent Social
Robots
Journal of e-Learning and Knowledge Society DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20368/1971-8829/1611
Abstract
Robotics in education is a promising new area: social robots have started to move into schools as part of educational/learning technologies, playing roles in educational settings that range from tutors, teaching assistants and learners, to learning companions and therapeutic assistants. This paper provides an overview of the main computational methods required to program a social robot and equip it with social intelligence. Some applications of social robots in the field of education are reported to show how the use of educational robots may innovate the learning process at different levels and in various contexts.

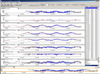
P. Buono, F. Balducci
MonitorApp: a web tool to analyze and visualize pollution data detected by an electronic nose
In Multimedia Tools and Applications.
pp.1-18. 17 May 2019. ISSN:1573-7721. DOI:10.1007/s11042-019-7676-3.
Abstract -
pdf -
bib
The analysis of air quality data may reveal the quality of life and can prevent dangers for the citizen health. Assuming that some chemical compounds in the air produce a bad smell, people may detect that something is going wrong acting as sensors that alerts potential risks. This work presents a visual analytics approach to support air quality experts in the analysis of data produced by electronic nose devices. The approach consists in setting workflows to manage and transform raw data offering clustering and visualization techniques to analyze such information. The analysis is supported by calendar, map and line graph visualization techniques also maneuvering the clustering attributes. The interactive map is used to show the position of monitoring stations in order to support making hypothesis related to the data source locations.
@Article{Buono2019,
author="Buono, Paolo
and Balducci, Fabrizio",
title="MonitorApp: a web tool to analyze and visualize pollution data detected by an electronic nose",
journal="Multimedia Tools and Applications",
year="2019",
month="May",
day="17",
abstract="The analysis of air quality data may reveal the quality of life and can prevent dangers for the citizen health. Assuming that some chemical compounds in the air produce a bad smell, people may detect that something is going wrong acting as sensors that alerts potential risks. This work presents a visual analytics approach to support air quality experts in the analysis of data produced by electronic nose devices. The approach consists in setting workflows to manage and transform raw data offering clustering and visualization techniques to analyze such information. The analysis is supported by calendar, map and line graph visualization techniques also maneuvering the clustering attributes. The interactive map is used to show the position of monitoring stations in order to support making hypothesis related to the data source locations.",
issn="1573-7721",
doi="10.1007/s11042-019-7676-3",
url="https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7676-3"
}
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, G. Desolda, R. Lanzilotti, M. Matera and A. Piccinno
Enabling End Users to Define the Behavior of
Smart Objects in AAL Environments
In: Leone A., Caroppo A., Rescio G., Diraco G., Siciliano P. (eds)
Ambient Assisted Living. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol
544. Springer, Cham. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-05921-7_8
Abstract -
pdf
In Ambient Assisted Living (AAL), Internet of Things
(IoT) technology is exploited to equip living environments with smart
objects that communicate with the outside world in an intelligent and
goal-oriented manner and can support the occupants’ activities.
Currently, providing such objects with new capabilities requires
several programming efforts. In this paper, we present an approach to
combine IoT technologies and End-User Development (EUD) paradigms and
tools to identify innovative scenarios where end-users are directly
involved in the creation and customization of the AAL systems they
use. We will present EFESTO, a Task Automation tool that offers novel
visual interaction paradigms to enable end users to easily express
rules for smart object configuration and discuss how the overall
approach can support daily practices of non-frail elderlies.
2018
P. Valdivia,
P. Buono, C.
Plaisant, J-D. Fekete, and N. Dufournaud
Using Dynamic Hypergraphs to Reveal the
Evolution of the Business Network of a 17th Century French Woman
Merchant
IEEE VIS 2018 - 3rd Workshop on Visualization for the Digital
Humanities, 21 October 2018, Berlin, Germany
Abstract -
pdf
Many digital humanity use cases require the analysis
of relationships between entities (e.g. people or countries). The
analysis of those relationships is particularly difficult when these
relations change over time. A common representations of such relations
is through graphs, which connect pairs of entities. However, in the
real world relationships are often more complex and can be better
described using hypergraphs (where edges can connect more than two
entities). In this paper, we present a digital humanity case study of
the analysis of people mentioned in 16th and 17th Century legal
documents, modeled as a dynamic hypergraph. We use a new
representation called Parallel Aggregated Ordered Hypergraph. Our
prototype implementation of Parallel Aggregated Ordered Hypergraph,
and the benefits of the PAOH representation are discussed.
V. Guchev,
P. Buono, C. Gena
Combining Multiple View Components for
Exploratory Visualization
IEEE VIS 2018 - VIS Posters, 21-26 October 2018, Berlin, Germany
Abstract
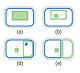
The analysis of structured complex data, such as
clustered graphbased datasets, may use a variety of visual
representation techniques and formats. Available tools and approaches
to exploratory visualization are built on integrated schemes for
simultaneous displaying of multiple aspects of objects and processes.
Such schemes partition screen space in multiple views and adopt
interaction patterns to focus on relevant items. From a technical
point of view, the interpretation of widely known concepts, such as
overview-plus-detail and focus-plus-context, is ambiguous. Therefore,
their implementation by UI design practitioners needs reviews and a
classification of the basic approaches to visual composition of
graphical representation modules. We propose a description of
components that characterize base, focus, context views, and provides
an overview of their multiple combinations.

P. Buono, A. Legretto, S.
Ferilli, S.Angelastro
A Visual Analytic approach to analyze Highway
Vehicular Traffic
2018 22nd International Conference Information Visualisation
(IV), Fisciano, Italy, 2018, pp. 204-209. doi: 10.1109/iV.2018.00044
Abstract -
pdf -
bib
The Italian National Police started a research on
vehicular traffic to improve road safety and reduce the number of
theft victims. In order to support the discovery of anomalous
behavior, this paper proposes a method for data analysis to
automatically detect relevant hypotheses, a data mining technique to
extract relevant information and a visualization technique. Traffic
flow analysis is a challenging and complex task, due to the huge size
of the data involved, thus falling in the realm of Big Data. Visual
Analytics tools reduce and improve the search by representing a large
amount of data in a small space through smart visualizations.
@INPROCEEDINGS{8564162,
author={P. Buono and A. Legretto and S. Ferilli and S. Angelastro},
booktitle={2018 22nd International Conference Information Visualisation (IV)},
title={A Visual Analytic Approach to Analyze Highway Vehicular Traffic},
year={2018},
volume={},
number={},
pages={204-209},
doi={10.1109/iV.2018.00044},
ISSN={2375-0138},
month={July}
}
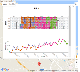
P. Buono, F. Balducci
A Web App for Visualizing Electronic Nose Data
22nd International Conference Information Visualisation (IV),
Fisciano, Italy, 2018, pp. 198-203. doi: 10.1109/iV.2018.00043
Abstract -
pdf -
bib
The analysis of air quality data may reveal the
quality of life and can prevent dangers for the citizen health. This
paper presents an approach for air quality data analysis, which
exploits Data Mining and InfoVis techniques to support the analysts
daily work. The proposed approach addresses data generated by the
electronic nose, a device that detects chemical compounds perceived by
humans through the smell. A working pipeline implements a workflow for
data processing with clustering techniques; an enhanced powerful
calendar visualization combined with more traditional line graph and
geo-referenced visualizations shows data to the analyst allowing to
detect temporal trends and making immediate comparisons.
@INPROCEEDINGS{8564161,
author={P. Buono and F. Balducci},
booktitle={2018 22nd International Conference Information Visualisation (IV)},
title={A Web App for Visualizing Electronic Nose Data},
year={2018},
volume={},
number={},
pages={198-203},
doi={10.1109/iV.2018.00043},
ISSN={2375-0138},
month={July}
}

P. Buono, F. Cassano, A.
Legretto, A. Piccinno
A Modular Pill Dispenser Supporting Therapies
at Home
In: Pautasso C., Sánchez-Figueroa F., Systä K., Murillo
Rodríguez J. (eds) Current Trends in Web Engineering. ICWE 2018. Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, vol 11153. Springer, Cham
Abstract -
pdf
Modern technologies support people’s life in multiple
contexts like the assistive one. The pervasiveness of the so-called
“Smart Objects”, related to the Internet of Things technologies, is
boosting this in many ways. The support for old people to take the
daily tablets through an automatic device is an example. This work
presents the prototype of a modular pill dispenser customized by end
users according to their specific therapy needs. The prototype is a
physical and modular set of pillboxes each containing the pills to be
assumed in a therapy. The presented scenario at a specific time, set
by the user, one or more pillboxes blink to alert the patient that is
pill time. If for a given time interval the patient do not take the
pill a sound notification is activated and plays for a given duration.
If still nothing happens then a notification is sent to the
caregiver’s smartphone. The behavior of the pill dispenser is defined
by the end user and can be modified any time. One peculiarity of the
pill dispenser is that the number of physical boxes are decided by the
user and can change any time to best fit the specific therapy. The
final goal of this work is to push not professional users, in
particular older people, to take advantages of new technologies to
improve their life.
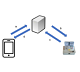
P. Buono, F. Cassano, A.
Legretto, A. Piccinno
EUDroid: a formal language specifying the
behavior of IoT devices
IET Software, 2018, IET Digital Library. DOI:
10.1049/iet-sen.2017.0347
Abstract -
pdf -
bib
Recent technologies are offering today many
possibilities to end users, which ask for continuous support in a
variety of situations. Internet of things (IoT) and the proliferation
of smart devices are offering many opportunities that raise the need
to standardize protocols for their interoperability and interaction
languages for their management. This paper proposes EUDroid, a system
composed of a mobile application and an IoT device used as a pill
reminder to allows the patients to correctly take their prescribed
drugs. A web server stores and manages the therapies that can be
de?ned by the end users. The web server also manages the communication
between the app and the device. In order to validate the management of
the therapies, a formal language has been proposed. It describes the
behavior of different components of the IoT device, such as LEDs or
buzzers, and de?nes when, with which delay, and for how long time a
given event will last, to manage technical concepts related to smart
devices for supporting them in following therapies more accurately.
@ARTICLE{
iet:/content/journals/10.1049/iet-sen.2017.0347,
author = {Paolo Buono},
author = {Fabio Cassano},
author = {Alessandra Legretto},
author = {Antonio Piccinno},
ISSN = {1751-8806},
language = {English},
title = {EUDroid: a formal language specifying the behavior of IoT devices},
journal = {IET Software},
year = {2018},
month = {June},
publisher ={Institution of Engineering and Technology},
copyright = {© Institution of Engineering and Technology},
url = {http://digital-library.theiet.org/content/journals/10.1049/iet-sen.2017.0347}
}

C. Ardito,
P. Buono, G.
Desolda, M. Matera
From Smart Objects to Smart Experiences: an
End-User Development Approach
International Journal of Human-Computer
Studies, International Journal of Human-Computer Studies.
Volume 114, 2018, Pages 51-68, ISSN 1071-5819.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2017.12.002
Abstract
The growing availability of smart objects is
stimulating researchers to investigate the Internet of Things (IoT)
phenomenon from different perspectives. The potential of this
technology is evident in different domains. In Cultural Heritage (CH),
it may enhance access to CH collections, in order to ensure a more
engaging visit experience and to increase the appropriation of CH
content by visitors. So far, research on IoT has primarily focused on
technical features of smart objects (e.g., how to program sensors and
actuators), while there are very few approaches trying to facilitate
the adoption of such a technology by end users. This lack limits the
social and practical benefits of IoT; it creates barriers in all those
usage scenarios where people would like to define the behavior of
smart objects but they might not have the required programming skills.
This is becoming evident in CH sites, where different stakeholders
would benefit from managing ecosystems of interoperable smart objects
to create enhanced visit experiences. This article presents a visual
composition paradigm that allows non-programmers to synchronize the
behavior of smart objects, thus determining more engaging user
experiences. It discusses how the paradigm suites the need of curators
and guides of CH sites to define smart visit experiences through which
visitors can acquire CH content by interacting with the surrounding
environment and the smart objects included in it. A serious game
designed with professional guides of CH sites is used as a case study
to show the potential of the presented approach.
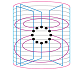
V. Guchev,
P. Buono, and C.
Gena
Towards intelligible graph data visualization
using circular layout
In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advanced
Visual Interfaces (AVI '18). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 63, 3
pages. DOI: https://10.1145/3206505.3206592
Abstract -
bib
Polar coordinates have been widely used in various
techniques of interactive data visualization. The spatial organization
through circular and radial layouts is implemented in a wide range of
statistical charts and plots and is applicable for space-filling
techniques and for node-link-group diagrams. Different arrangements of
dots, lines and areas in polar coordinates create grids for data
distribution, aggregation and linking. This work is devoted to the
study of visual notations of data and their relationships and proposes
an outline of their application in designing node-link-group diagrams,
in order to arrange the geometric solutions at functional and logical
levels of the visual representation.
@inproceedings{Guchev:2018,
author = {Guchev, Vladimir and Buono, Paolo and Gena, Cristina},
title = {Towards Intelligible Graph Data Visualization Using Circular
Layout},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on
Advanced Visual Interfaces},
series = {AVI '18},
year = {2018},
isbn = {978-1-4503-5616-9},
location = {Castiglione della Pescaia, Grosseto, Italy},
pages = {63:1--63:3},
articleno = {63},
numpages = {3},
url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3206505.3206592},
doi = {10.1145/3206505.3206592},
acmid = {3206592},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
keywords = {circular and radial layout, data visualization, graph
drawing, guidelines, node-link-group diagram},
}

F. Balducci and
P. Buono
Building a qualified annotation dataset for
skin lesion analysis through gamification
In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advanced
Visual Interfaces (AVI '18). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 36, 5
pages. DOI: https://10.1145/3206505.3206555
Abstract -
bib
The deep learning approach has increased the quality
of automatic medical diagnoses at the cost of building qualified
datasets to train and test such supervised machine learning methods.
Image annotation is one of the main activity of dermatologists and the
quality of annotation depends on the physician experience and on the
number of studied cases: manual annotations are very useful to extract
features like contours, intersections and shapes that can be used in
the processes of lesion segmentation and classification made by
automatic agents. This paper proposes the design of an interactive
multimedia platform that enhance the annotation process of medical
images, in the domain of dermatology, adopting gamification and "games
with a purpose" (GWAP) strategies in order to improve the engagement
and the production of qualified datasets also fostering their sharing
and practical evaluation. A special attention is given to the design
choices, theories and assumptions as well as the implementation and
technological details.
@inproceedings{Balducci:2018,
author = {Balducci, Fabrizio and Buono, Paolo},
title = {Building a Qualified Annotation Dataset for Skin Lesion
Analysis Through Gamification},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on
Advanced Visual Interfaces},
series = {AVI '18},
year = {2018},
isbn = {978-1-4503-5616-9},
location = {Castiglione della Pescaia, Grosseto, Italy},
pages = {36:1--36:5},
articleno = {36},
numpages = {5},
url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3206505.3206555},
doi = {10.1145/3206505.3206555},
acmid = {3206555},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
keywords = {GWAP, annotation, dermatology, gamification, machine
learning},
}

T. Catarci, M. Amendola, F. Bertacchini, E.
Bilotta, M. Bracalenti,
P. Buono, A. Cocco, M. F.
Costabile, G. Desolda, F. Di Nocera, S. Federici, G. Gaudino, R.
Lanzilotti, A. Marrella, M. Laura Mele, P. S. Pantano, I. Poggi, and L.
Tarantino
Digital interaction: where are we going?
In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advanced
Visual Interfaces (AVI '18). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 4, 5 pages.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3206505.3206606
Abstract -
bib
In the framework of the AVI 2018 Conference, the
interuniversity center ECONA has organized a thematic workshop on
"Digital Interaction: where are we going?". Six contributions from the
ECONA members investigate different perspectives around this thematic.
@inproceedings{Catarci:2018,
author = {Catarci, Tiziana and Amendola, Massimo and Bertacchini,
Francesca and Bilotta, Eleonora and Bracalenti, Marco and Buono, Paolo
and Cocco, Antonello and Costabile, Maria Francesca and Desolda,
Giuseppe and Di Nocera, Francesco and Federici, Stefano and Gaudino,
Giancarlo and Lanzilotti, Rosa and Marrella, Andrea and Mele, Maria
Laura and Pantano, Pietro S. and Poggi, Isabella and Tarantino,
Laura},
title = {Digital Interaction: Where Are We Going?},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on
Advanced Visual Interfaces},
series = {AVI '18},
year = {2018},
isbn = {978-1-4503-5616-9},
location = {Castiglione della Pescaia, Grosseto, Italy},
pages = {4:1--4:5},
articleno = {4},
numpages = {5},
url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3206505.3206606},
doi = {10.1145/3206505.3206606},
acmid = {3206606},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
keywords = {accessibility, human factors in cybersecurity, multimodal
interaction, participatory design, usability evaluation, user
experience, visual interfaces},
}
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M.F.
Costabile, G. Desolda, R. Lanzilotti, M. Matera, A. Piccinno
Towards Enabling Cultural-Heritage Experts to
Create Customizable Visit Experiences
In: B.N. De Carolis, C. Gena, T. Kuflik, A. Origlia, G. E.
Raptis. Proceedings of the AVI-CH 2018 - Advanced visual interfaces for
cultural heritage. CEUR workshop proceedings, vol. 2091, p. 2.1-2.5,
ISSN: 1613-0073
Abstract -
pdf
In recent years, smart objects are increasingly
pervading the environments we live in. Several studies highlight that
Cultural Heritage (CH) is a very promising domain for IoT adoption,
since this technology can favor the definition of smart visit
experiences that engage visitors by allowing them to acquire CH
content while interacting with the surrounding smart environment and
the smart objects included in it. This paper presents new End-User
Development approaches and the related abstractions that can support
CH experts to create customizable visit experiences within museums and
other cultural sites.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M.F.
Costabile, G. Desolda, R. Lanzilotti, M. Matera, A. Piccinno
An end user development approach for crafting
smart interactive experiences
In: Florian Müller Dirk Schnelle-Walka Sebastian Günther Markus
Funk. Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Interacting with Smart Objects
(SmartObjects). CEUR workshop proceedings, vol. 2082, p. 23-30, ISSN:
1613-0073
Abstract -
pdf -
bib
Despite the advantages that Internet of Things (IoT)
technology offers, there are still important issues to be solved to
increase its practical impact. The opportunities offered by IoT can be
amplified if new approaches, based on high-level abstractions and
adequate interaction paradigms, are conceived to involve directly
non-technical users in configuring the behavior of their smart
objects. In this paper, we present our End-User Development approach,
which we would like to discuss at the workshop together with the
challenges our future research implies.
@inproceedings{ArditoEtAl:SmartObjects2018,
title = {An End-User Development Approach for Crafting Smart Interactive Experiences},
author = {Carmelo Ardito and Paolo Buono and Maria Francesca Costabile and Giuseppe Desolda and Rosa Lanzilotti and Maristella Matera and Antonio Piccinno},
pages = {23--30},
url = {http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2082/#paper_4},
crossref = {SmartObjects2018},
}
@proceedings{SmartObjects2018,
booktitle = {6th Workshop on Interacting with Smart Objects (SmartObjects)},
title = {Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Interacting with Smart Objects (SmartObjects)},
year = 2018,
editor = {Florian Müller and Dirk Schnelle-Walka and Sebastian Günther and Markus Funk},
number = 2082,
series = {CEUR Workshop Proceedings},
address = {Aachen},
issn = {1613-0073},
url = {http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2082/},
venue = {Montreal, Canada},
eventdate = {2018-04-21},
}

P. Buono, F. Cassano, A.
Legretto, A. Piccinno
A Homemade Pill Dispenser Prototype Supporting
Elderly
In: Garrigós I., Wimmer M. (eds) Current Trends in Web
Engineering. ICWE 2017. LNCS 10544, pp. 120-124. DOI:
10.1007/978-3-319-74433-9_10
Abstract -
pdf -
bib
People, and mainly elderly people, need a continuous
support for different reasons. Recent technologies are offering many
possibilities that was not possible to conceive in the past. In
particular, the proliferation of IoT devices raise the need to
standardize protocols and interaction languages. The aim of this work
is to create a device for the management of pills according to the
user's therapy, with Internet of things (IoT) devices and by allowing
users to manage the pill dispenser by themselves. The work falls into
two main areas of current research: the End-user development (EUD) and
the Internet of things (IoT). The main issue we cope with such device
is to allow the different therapies for each person and for each drug.
We propose the EUDroid system, which provides the end user with the
possibility to easily activate LEDs and buzzer related to pills from
the users' smartphone. The user chooses the type of pill to be
associated to each LED, the day and time of activation and some other
property. A formal language to configure the device has been adopted
in order to allow users to build complex conditions for remind to
follow the therapy.
@inbook{RN1060,
author = {Buono, Paolo and Cassano, Fabio and Legretto, Alessandra and
Piccinno, Antonio},
title = {A Homemade Pill Dispenser Prototype Supporting Elderly},
booktitle = {Current Trends in Web Engineering (ICWE)},
editor = {Garrigós, Irene and Wimmer, Manuel},
series = {Current Trends in Web Engineering},
publisher = {Springer International Publishing},
address = {Cham},
volume = {LNCS },
pages = {120-124},
ISBN = {978-3-319-74433-9},
DOI = {10.1007/978-3-319-74433-9_10},
url =
{https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-319-74433-9_10},
year = {2018},
type = {Book Section}
}

C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M.
Costabile, D. Caivano, G. Desolda, R. Lanzilotti, M. Matera, A. Piccinno
Exploiting ICT to Create Smart Visit
Experiences at Cultural Heritage Sites
In: 7mo convegno annuale AIUCD 2018 - Patrimoni culturali
nell'era digitale. Memorie, culture umanistiche e tecnologie. Bari,
January 31st - February 2nd, 2018. pp. 46-50
Abstract -
pdf
Information and communication technologies have a
great potential to increase awareness and appreciation of cultural
heritage. In the last decade, at the Computer Science Department of
the University of Bari (Italy), we have been working to the design,
development and evaluation of software systems supporting people
during their visits to historical sites and museums, with the goal of
improving the overall user experience. We focused on pervasive games
to offer an engaging way to experience the cultural heritage site.
This article briefly describes some games we developed and presents
some of our new recent approaches. Specifically, we are investigating
possible use of the Internet of Things (IoT) technology, as well as
Mixed Reality, in order to ensure a more engaging visit experience and
to increase the appropriation of CH contents by visitors.
2017

M. Fiorentino, P. Buono, A. E. Uva, V. M.
Manghisi, M. Gattullo, A. Boccaccio, G. Monno
ARSAS: active aging of the worker by spatial
augmented reality
Italian Journal of Occupational and Environmental
Hygiene. Vol 8, No 4 (2017): pages 120-164. eISSN: 2464-8817
Abstract -
www
ARSAS (Augmented reality supported Aging system), is a
system developed for maintaining the work ability of older workers in
industrial context. ARSAS integrates two main technologies the “video
summarization” (automatic summary of video streams) and the spatial
augmented reality. The system is able to project on the workbench
surfaces pre-recorded instruction video and / or technical information
from digital manuals. The operator performs his tasks normally, but is
videotaped and, if necessary, assisted in his activities by AR
instructions and multimedia. The main advantages of the system are: to
provide a digital memory and reduce the cognitive load of the
operator. A second benefit is that the system can easily acquire and
store the knowledge of skilled and\or experienced workers in
semi-automatic way. The preliminary tests showed a significant
reduction in the risk of errors and execution times.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, G.
Desolda, M. Matera
Empowering CH Experts to Produce IoT-enhanced
Visits
In Adjunct Publication of UMAP 2017, M. Tkalcic, D. Thakker, P.
Germanakos, K. Yacef, C. Paris, and O. Santos (Eds.). ACM, New York, NY,
USA, 327-328. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3099023.3099089
Abstract -
pdf
This demo presents a platform for the definition of
IoT-enhanced visits to Cultural Heritage (CH) sites. The platform is
characterized by an End-User Development paradigm applied to the
Internet of Things technologies and customized for the CH domain. It
allows different stakeholders to configure the behavior of smart
objects in order to create more engaging visit experience and to
increase the appropriation of CH content by visitors.
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, G. Desolda, R. Lanzilotti, M. Matera
Advanced Technologies for Enabling Smart Visit
Experiences to Cultural Heritage Sites
i-cities 2017, September 27-29 2017, Bari, Italy
C. Ardito, M. T. Baldassarre, P. Buono,
D. Caivano, G. Desolda, M. Morga, A. Piccinno
Interaction Design in Mixed Reality: Case
Studies and Challenges
i-cities 2017, September 27-29 2017, Bari, Italy

C. Ardito, M. T. Baldassarre,
P. Buono,
D. Caivano, G. Desolda, M. Morga, A. Piccinno
Mid-Air Gestures in Mixed Reality: Issues and
Challenges
Multimodal 2017 workshop, September 18 2017, Cagliari, Italy
Abstract
Mixed Reality (MR) visual displays are a particular
subset of Virtual Reality technology. They combine the merging of real
and virtual worlds somewhere along the "virtuality continuum" which
fully connects real environments with virtual ones. These devices
promise a more natural interaction thanks to mid-air gestures.
However, they implement interaction techniques that are often rough,
inaccurate and unnatural, because they are mediated by mechanisms
designed for PCs and mobile devices. This paper reports on a set of MR
interaction experiences we collected during the last years, reflecting
on recurrent issues identified and analyzing some possible solutions.
The paper concludes with a brief discussion of an ongoing project that
exploits MR devices to interact with smart objects installed in
museums and archaeological parks.

P. Valdivia, P. Buono, J.-D. Fekete
Hypenet: Visualizing Dynamic Hypergraphs
EuroVis 2017, 12-16 June 2017, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 33-35. DOI:
10.2312/eurp.20171162
Abstract -
bib
We present Hypenet, a novel technique to visualize
dynamic hypergraphs. Such structures can model multiple types of data,
such as computer networks with multiple destination addresses
(multicast) or co-authorship networks with multiple authors per
article. Hypenet visualizes the evolving topology of the hypergraph in
a compact way, allowing users to detect patterns and inconsistencies.
We describe our technique and show how it applies to the case of the
history of publications of the Eurovis conference, revealing
interesting patterns that can contribute to tell a story about data
and create hypotheses.
@inproceedings {eurp.20171162,
booktitle = {EuroVis 2017 - Posters},
editor = {Anna Puig Puig and Tobias Isenberg},
title = {{Hypenet: Visualizing Dynamic Hypergraphs}},
author = {Valdivia, Paola and Buono, Paolo and Fekete, Jean-Daniel},
year = {2017},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
ISBN = {978-3-03868-044-4},
DOI = {10.2312/eurp.20171162}
}
2016
C. Ardito, M. F. Costabile, G. Desolda, M.
Matera,
P. Buono
A Meta-design Approach to Support Information
Access and Manipulation in Virtual Research Environments
M.X. Bornschlegl, F.C. Engel, R. Bond, M.L. Hemmje (Eds.):
AVI-BDA 2016, LNCS 10084, pp. 115–126, 2016. DOI:
10.1007/978-3-319-50070-6_9
Abstract -
pdf
Virtual Research Environments (VREs) are distributed
and dynamic software environments that foster the collaboration of
people from di?erent disciplines by supporting the accomplishment of
complex research tasks. VREs lack e?cient and e?ective user interfaces
able to satisfy the needs of the di?erent types of people
collaborating in performing certain tasks. Thus, a great challenge
that VREs have to address is user diversity, which arises from
di?erent factors such as cultural background of users, their reasoning
strategies, the way they carry out their tasks in their daily
practices, and the languages and notations they are familiar with.
This paper provides a solution to this challenge by proposing to
create VREs that exploit the meta-design approach we have developed to
design interactive systems that address user diversity. We then
describe a mashup platform, built according to the meta-design
approach, which supports non-technical users in accessing and
manipulating information in VREs by enabling them to extract contents
from heterogeneous sources and manipulate such content in their
personal interactive environments, thus creating new content that can
be shared among people collaborating to a task in a VRE. Finally, it
is brie?y discussed how this platform can be useful in some phases of
the recently proposed model of Information Visualization for Big Data.
P. Buono
Visualizing Transportation Routes for Data
Analysis in Logistics
In Proceedings of the on Distributed Multimedia Systems (DMS
'16), Giuseppe Polese and Vincenzo Deufemia (Eds.). KSI Research Inc.
and Knowledge Systems Institute Graduate School, 210-215.
DOI=10.18293/DMS2016-040
Abstract -
pdf
Logistics activities refer to transporting materials
and/or storing them in specific warehouse (platforms) for a given
period of time. Typical problems are related to route and vehicle load
optimization and monitoring of transportation conditions. GPS
availability in the vehicles allows transportation companies to
remotely check if vehicles are on schedule. Such information is often
related to a single shipment. This paper presents a web tool which
aims to support analysts through an interactive visualization
technique that shows all routes performed by the vehicles in a given
period of time on a geographic map. The tool allows analysts to
perform explorative analysis in order to obtain information that
otherwise is difficult to get. Various filters help them to reduce the
visualized data to a manageable quantity. The interface is simple,
complex queries can be executed by specifying a few parameters and
performing zoom & pan gestures on the map
P. Buono, R. Lanzilotti, M.
Matera (Eds.). 2016.
Proceedings of the International Working
Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces. ACM, New York, NY, USA
ISBN: 978-1-4503-4131-8
ACM website
P. Buono
A Circular Visualization Technique for
Collaboration and Quantifying Self
In Proceedings of the International Working Conference on
Advanced Visual Interfaces (AVI '16), Paolo Buono, Rosa Lanzilotti, and
Maristella Matera (Eds.). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 348-349. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2909132.2926091
Abstract
People awareness in various contexts has been widely
considered in the literature. A form of awareness is the
quantification of self, which requires a number of conditions to be
implemented. The most important are: producing, computing and making
sense of data. Sensors produce data at very high rates. A lot of
research, in the field of data bases, has focused on how to store and
compute data efficiently. Data presentation is still challenging,
because the possibilities of producing interactive visualizations on
the Web and on different devices are increasing. The contribution of
this demo paper is to propose a visualization technique and a
web-based tool enabling the visualization of personal data produced
during the 24 hours of the day. The aim of this tool is to help people
to understand their own behavior. Such data can also be compared with
other people's data to improve the analysis. This demo focuses on two
main contexts: visualizing working data of a group of people living in
different time zones in order to improve the awareness of the behavior
of the group; visualizing energy consumption data in order to provide
an idea of the behavior of people in the domestic context. The data
for the first example are gathered from the activity people perform
with their computer (e.g. email, chat, keyboard strokes) while the
data of the second context are gathered from a low-cost Arduino device
capable of providing instant electricity consumption information.
2015
P. Buono
A Low Cost System for Home Energy Consumption
Awareness
Proc. of Workshop and Poster Papers of 12th European Conference,
AmI 2015, Athens, Greece, November 11-13, 2015. CEUR Workshop
Proceedings. Vol. 1528. ISSN 1613-0073.
Abstract -
pdf
One of the main reasons of domestic energy waste is due
to occupants' habits, since they are often not aware of the energy
they are consuming. This paper presents a low cost system for home
energy consumption awareness. The first prototype considers electrical
energy and uses only two sensors: one to monitor energy produced by
solar panels and one to monitor consumed energy. A visualization shows
people their consumption patterns in order to make them aware of
energy consumption and change their habits to save energy.

P. Buono, A. Cuzzocrea
A Collaborative Framework for Supporting
Combined Visualization of Activities Across Time Zones
Proc. of International Conference on Collaboration Technologies
and Systems (CTS 2015). Atlanta, Georgia, June, 1-5, 2015, pp. 226-232,
IEEE, ISBN: 978-1-4673-7646-4. DOI:
10.1109/CTS.2015.7210427
Abstract
Collaboration today is often done among people from
different countries located in different time zones. Even if daily
activity patterns are very similar, the displacement of the time of
the day, due to the time zone can reduce the possibilities to have a
meeting or contact a collaborator. This paper proposes a visualization
technique that shows to different users the activity patterns of
collaborator in order to improve the awareness in the team. The
representation shows several data types in a 24h clock metaphor. The
information conveyed discussed in the paper are email, instant
messaging, presence at the computer, scheduled activities in a time
windows of 24h, which can be extended to 48h.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, G. Desolda
Interaction with Large Displays: A Survey
ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 47, 3,
Article 46, February 2015. DOI:
10.1145/2682623
Abstract -
pdf
Large interactive displays are increasingly placed in
public (or semipublic) locations, including museums, shops, various
city settings, and offices. This article discusses the evolution of
such displays by looking at their use and analyzing how they are
changing the concept of human-computer interaction through new
modalities. By surveying the literature on systems using these
displays, relevant features were identified and used as classification
dimensions. The analysis provided may inform the design and
development of future installations. A discussion on research
challenges concludes the article.
2014
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, D.
Caivano, M. F. Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, Y. Dittrich
Human-Centered Design in Industry: Lessons from
the Trenches.
IEEE COMPUTER, 47(12), December 2014, pp.
86-89.
DOI:
10.1109/MC.2014.355.
- abstract here -
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, R.
Lanzilotti
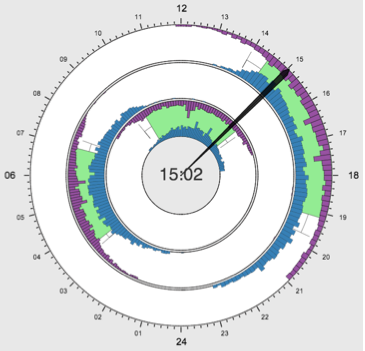
A Circular Visualization of People's Activities
in Distributed Teams
Journal of Visual Languages & Computing, 25(6),
December 2014, pp. 903-911.
DOI:
10.1016/j.jvlc.2014.10.025
Abstract -
pdf
When working in distributed teams, it is very important
to be aware of the activities of all members, since it provides hints
about when they might be available for collaboration. We propose a
novel visualization technique that combines several representations to
show the daily patterns of team members' activities. It uses a 24 h
circular display to facilitate international collaboration across time
zones. Current calendar information can be compared to the typical
patterns and reveal likely availability. User studies evaluating the
tool that implements the proposed technique are reported and
discussed.
P. Buono and G. Desolda
Visualizing collaborative traces in distributed
teams
Proc. of Advanced Visual Interfaces (AVI 2014). Como, Italy, May, 27-30,
2014, pp. 343-344, NEW YORK: ACM, ISBN: 978-1-4503-2775-6
Abstract -

The evolution of communication technologies provides
sup- port to the collaboration of people that work in distributed
teams. Group awareness is an important requirement for ac- tivity
coordination, since understanding the activities of the others
provides the context for the individual own activities and gives
indications on how individual contributions are rel- evant to the
team. This poster proposes a novel information visualization technique
that aims at supporting awareness in distributed teams. Collaborative
traces of team mem- bers are visualized in order to show which one is
the most available and responsive.
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno, L. Zhu
On the transferability of a meta-design model
supporting end-user development.
Universal Access in the Information Society,
14(2). doi: 10.1007/s10209-013-0339-7

C. Ardito,
P. Buono, D.
Caivano, M. F. Costabile, R. Lanzilotti
Investigating and promoting UX practice in
industry: an experimental study.
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,
72(6), June 2014, pp. 542--551. Elsevier, Maryland Heights, Missouri,
USA. ISSN 1071-5819.
Abstract -
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2013.10.004
The efforts of addressing user experience (UX) in
product development keep growing, as demonstrated by the proliferation
of workshops and conferences bringing together academics and
practitioners, who aim at creating interactive software able to
satisfy their users. This special issue focuses on 'Interplay between
User Experience Evaluation and Software Development', stating that the
gap between human- computer interaction and software engineering with
regard to usability has somewhat been narrowed. Unfortunately, our
experience shows that software development organizations perform few
usability engineering activities or none at all. Several authors
acknowledge that, in order to understand the reasons of the limited
impact of usability engineering and UX methods, and to try to modify
this situation, it is fundamental to thoroughly analyze current
software development practices, involving practitioners and possibly
working from inside the companies. This article contributes to this
research line by reporting an experimental study conducted with
software companies. The study has confirmed that still too many
companies either neglect usability and UX, or do not properly consider
them. Interesting problems emerged. This article gives suggestions on
how they may be properly addressed, since their solution is the
starting point for reducing the gap between research and practice of
usability and UX. It also provides further evidence on the value of
the research method, called Cooperative Method Development, based on
the collaboration of researchers and practitioners in carrying out
empirical research; it has been used in a step of the performed study
and has revealed to be instrumental for showing practitioners why to
improve their development processes and how to do so.
2013
P. Buono, G. Desolda, R.
Lanzilotti
A telementoring system for supporting
laparoscopic surgeries.
Proc. of the Annual Conference of the Associazione Italiana per il
Calcolo Automatico - AICA, Fisciano, 18-20 September, 2013.
ISBN: 978-88-98091-16-4
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno
Usability in software development company
practices.
Proc. of the Annual Conference of the Associazione Italiana per il
Calcolo Automatico - AICA, Fisciano, 18-20 September, 2013.
ISBN: 978-88-98091-16-4
M. T. Artese, L. Biocca, P. Buono,
I. Gagliardi, A. Lerario, N. Maiellaro, N. Paraciani
MU.S.A. - Must See Advisor' Project: a Cultural
Heritage Booster.
Proc. of 6th International Congress on Science and Technology for the
Safeguard of Cultural Heritage in the Mediterranean Basin, pp. 244-245.
Athens, Greece, 22nd-25th October 2013.
ISBN: 978-88-97987-01-7
P. Buono, G. Desolda, R.
Lanzilotti
Scenes extraction from telementored surgery
videos
Proc. of International Conference on Distributed Multimedia Systems (
DMS 2013).
Brighton, UK, August 8-10, 2013, SKOKIE: Knowledge Systems Institute
Abstract -
pdf
The huge amount of videos, available for various
purposes, makes video editing software very important and popular
among people. One of the uses of video in medicine is to store
surgical operations for educational or legal purposes. In particular,
in telemedicine, the exchange of audio and video plays a very
important role. In most cases, surgeons are inexpert in video editing;
moreover, the user interface of such software tools is often very
complex. This paper presents a tool to extract important scenes from
surgery videos. The goal is to enable surgeons to easily and quickly
extract scenes of interest.

E. Andriani, M. Brattoli,
P. Buono,
G. de Gennaro, L. de Gennaro
Development of a Tool for Industrial
Atmospheric Emission Management in the Apulia Region.
Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, March 2013,
Vol. 12, No. 3, pp. 429-434. ISSN: 1582-9596, eISSN: 1843-3707
Abstract
-
EEMJ - IF 2014: 1.258
Atmospheric emission inventories are useful tools to
support informed decision making in air quality management. In the
framework of Apulia Region emission inventory, a tool for the
industrial atmospheric emission management called Territorial
Emissions Cadastre (CET) was developed. CET is a Web-based system able
to store all data related to the industrial plants and to perform
spatial queries; its components are used for synchronizing, exporting
and querying the underlined database. CET also enables access to
information that is useful to support air quality monitoring experts
in their decision-making process. An innovative feature of CET is
CETGE. It allows the users to visualize the industrial plants and the
associated emissions in Google Earth, which provides an effective tool
to display the most relevant industrial emission sources on a Regional
area view. CETGE can be used by the stakeholders to evaluate and
present alternative solutions for areas characterized by high impact
emission sources.
M. Costabile,
P. Buono
Principles for Human-Centred Design of IR
Interfaces.
Agosti, M., Ferro, N., Forner, P., Muller, H., Santucci, G. (eds.),
Information
Retrieval Meets Information Visualization, vol. LNCS 7757, pp.
28-47. Springer Berlin Heidelberg
Abstract -
pdf
-
Springer
Since the '80s, Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)
researchers have performed a lot of work to identify principles,
techniques, and methodologies that can support design, evaluation and
implementation of interactive systems that fulfill needs and
expectations of their users. This chapter discusses concepts, such as
usability and user experience, which are of great importance for the
success of interactive systems, illustrating how Human-Centred Design
is fundamental to create successful user interfaces. Principles
proposed by the HCI community to support interface design are
presented, analyzing the principles that have a major impact on IR
interfaces.
2012

C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti
Are software companies aware of UX?
International Workshop on the Interplay between User Experience (UX)
Evaluation and System Development (I-UxSED 2012). NordiCHI 2012,
Copenhagen, Denmark, pp. 10-13
Abstract -
pdf
The efforts of addressing user experience (UX) in
product development keeps growing, as demonstrated by the
proliferation of workshops and conferences bringing together academics
and practitioners, who aim at creating interactive software able to
satisfy their users. Unfortunately, human-centred design and methods
addressing usability and UX are always mentioned in research papers
but yet very seldom applied in the current practice of software
development in industry. In this paper, some findings of studies we
have recently performed with software companies are reported. They
show that either companies still neglect usability and UX, or they do
not properly address them. Thus, in this workshop that seems to
consider UX evaluation as a usual practice and aims to optimize the
impact of UX evaluation feedback on software development, our
provocative statement is: Are software companies (at least) aware of
UX? The studies summarized in this paper show that, in many cases, the
answer is NO. We are working to overcome the current situation and the
paper concludes by providing some suggestions to fill the gap between
research and practice of UX.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M.F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, S. Fioriello
New Channels, Creativity, EUD for creating
Engaging Experiences of Cultural Heritage.
Workshop on Creative Design for Interdisciplinary Projects on Cultural
Heritage. October 4th, Innsbruck, Austria
Abstract -
pdf
The goal of our research in Cultural Heritage is to
create applications on advanced devices, in order to provide engaging
experiences that can foster people interest in Cultural Heritage. In
this paper, we highlight some features of the developed applications
to show how creativity, new communication channels and End-User
Development (EUD) are used to reach our research goal.

P. Buono, M. F. Costabile
Insights on the development of visual tools for
analysis of pollution data.
Proc. of International Conference on Distributed Multimedia Systems (
DMS 2012).
Miami, August 9-11, p. 54-59, Skokie, IL 60076, USA:Knowledge Systems
Institute, ISBN: 1-891706-32-2
Abstract -
pdf
Developing visual tools that support data analysis in a
specific application domain requires a careful investigation in order
to understand needs and expectations of people who will use such
tools. The domain experts addressed in this paper are chemists
specialized in environmental data analysis. Their main activity is to
detect and monitor chemical compounds in the air through many devices
in order to detect anomalies or prevent risks. One of the main
problems that chemists face is the analysis of the huge amount of data
produced by devices. They perform explorative data analysis and are
willing to use software tools that can help them to get insights from
data. This paper reports the experience in working with chemists to
identify interactive visual tools that can be useful for their
purposes. It provides insights on the difficulty of creating systems
that users find really useful for their work, even when users
participate in the design team. Because of the complexity of the
considered problem and the fact that people are unable to make
explicit all their needs and requirements, the identification of
proper tools resulted very challenging.
E. Andriani, M. Brattoli,
P. Buono,
G. de Gennaro, L. de Gennaro, A. Mazzone.
A GIS tool for atmospheric emission management
in South of Italy.
Fresenius Environmental Bulletin. 11(2012) ISSN: 1018-4619.
Abstract
Emission inventories are useful tools in air quality
management policies. In the framework of Apulia Region (South of
Italy) inventory, the Territorial Emission Cadastre (CET) was
developed. CET stores the huge amount of data concerning industrial
plants. In order to easily interact with input data and analyze them,
a graphical user interface that includes a GIS (Geographical
Information System) component was integrated (CETGIS). This paper
focuses on the development of CETGIS and analysis possibilities
provided by GIS technology, which allow decision makers to monitor the
state of air quality and to evaluate the targets to be achieved.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno.
End users as co-designers of their own tools and products.
Journal of Visual Languages and Computing 23(2), pp. 78-90. doi:
10.1016/j.jvlc.2011.11.005.
Abstract
In our Age of exponential technological advance, recent
developments are determining an evolution of end users from passive
information consumers into information producers. Users are
increasingly willing and, indeed, determined to shape the software
they use to tailor it to their own needs. Based on a brief review of
research activities we performed in the last decade, this paper
analyzes some challenges that software designers face to comply with
the new roles of end users in the software life cycle, and discusses
how to provide end users with software environments that empower them
to become co-designers of their own tools and products. The examples
reported in the paper show why and how end users are involved in
design activities in various application domains.
2011

S. Kandel, J. Heer, C. Plaisant, J. Kennedy, F.
van Ham, N. Henry Riche, C. Weaver, B. Lee, D. Brodbeck,
P.
Buono.
Research directions in data wrangling: Visualizations and
transformations for usable and credible data.
Information Visualization Journal, vol. 10(4). October 2011, pp.
271-288, SAGE. doi:10.1177/1473871611415994. ISSN: 1473-8716
Abstract -
pdf - IF 2011:
0.889
In spite of advances in technologies for working with
data, analysts still spend an inordinate amount of time diagnosing
data quality issues and manipulating data into a usable form. This
process of 'data wrangling' often constitutes the most tedious and
time-consuming aspect of analysis. Though data cleaning and
integration arelongstanding issues in the database community,
relatively little research has explored how interactive visualization
can advance the state of the art. In this article, we review the
challenges and opportunities associated with addressing data quality
issues. We argue that analysts might more effectively wrangle data
through new interactive systems that integrate data verification,
transformation, and visualization. We identify a number of outstanding
research questions, including how appropriate visual encodings can
facilitate apprehension of missing data, discrepant values, and
uncertainty; how interactive visualizations might facilitate data
transform specification; and how recorded provenance and social
interaction might enable wider reuse, verification, and modification
of data transformations.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile.
Involving End Users to Create Software Supporting Visits to Cultural
Heritage Sites.
In: P. Marti, A. Soro, L. Gamberini, and S. Bagnara (Eds.). Proc. of the
9th ACM SIGCHI Italian Chapter International Conference on
Computer-Human Interaction: Facing Complexity. pp. 157-163, ACM, New
York, NY, USA., ISBN/ISSN: 978-1-4503-0876-2
Abstract -

Cultural heritage provides a great legacy that more and
more people should experience and appreciate. Information and
communication technologies may contribute to increasing awareness in
cultural heritage. In the last few years we have developed several
applications aimed at supporting visits to cultural heritage sites.
Such applications depends very much on the visitors they address, the
devices they are implemented on, etc. In this paper, we illustrate the
design approach we have adopted, which takes into account an end-user
development perspective in order to allow different stakeholders to
contribute to the design. The Cultural Heritage Resources (CHeR)
model, encompassing all the entities involved in the design process,
including the stakeholders, the digital resources to be shown, the
different types of visitors, the relationships between these entities
is described. It is at the basis of a software framework that has been
developed to allow different stakeholders to contribute in the design
of the final application. It is shown how this framework is used to
create engaging applications in cultural heritage.
C. Ardito, B. R. Barricelli,
P. Buono,
M. F. Costabile, A. Piccinno, S. Valtolina, L. Zhu.
An Ontology-Based Approach to Product Customization.
In: M. F. Costabile, Y. Dittrich, G. Fischer, A. Piccinno. End-User
Development. vol. LNCS 6654, pp. 92-106, Heidelberg: Springer,
ISBN/ISSN: 978-3-642-21529-2, doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21530-8_9
Abstract -
Springer
Mass customization refers to the increase in variety
and customization of the manufactured products and services. It is now
economically feasible thanks to the availability of computer-aided
manufacturing systems, which allow people to customize standard
products, and to Internet, through which many online retailers now
operate, thus eliminating the constraints of physical shelf space and
other bottlenecks of distribution that, in past years, prevented the
production of niche products because of their high production costs.
To permit mass customization, several software-based product
configurators are available on the Web: they guide people in adapting
a product to their needs and desires. A drawback of such configurators
is the limited range of changes permitted. We present in this paper a
system that gives people more freedom in creating products that best
fit their desires, thanks to the use of an ontology, which models the
possible product compositions that users can perform. The proposed
solution is shown through a case study, which refers to furniture
production.
C. Ardito, B. R. Barricelli,
P. Buono,
M. F. Costabile, A. Piccinno, S. Valtolina, L. Zhu.
Visual Mediation Mechanisms for Collaborative Design and Development.
In: C. Stephanisid. Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction.
Design for All and eInclusion. vol. LNCS 6765, pp. 3-11, Heidelberg:
Springer, ISBN/ISSN: 978-3-642-21671-8, doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21672-5_1
Abstract -
Springer
Collaborative design involving end users has emerged as
a response to the needs felt by various organizations of adapting
software to specific environments and users. During time, users and
environments evolve; this is another reason why software has to be
modified. Different stakeholders, including consultants, designers
internal to the organization and, recently, end users, have to
collaborate among themselves, and possibly with the software
providers, to shape software. Such stakeholders face fundamental
challenges in learning how to communicate and in building a shared
understanding. Researchers are now addressing such challenges. This
paper contributes to this innovative research by formally defining
visual mediation mechanisms for collaborative design. A case study
illustrating their application is discussed.

P. Buono.
Analyzing video produced by a stationary surveillance camera.
Proc. of International Conference on Distributed Multimedia Systems (
DMS 2011).
Florence, Italy, August 18-20, 2011, SKOKIE: Knowledge Systems
Institute, pp. 140-145, ISBN/ISSN: 1-891706-30-6
Abstract -
pdf -
proceedings
DMS 2011 (pdf ~25MB)
Today surveillance systems are everywhere. Human
observers watching live videos of specific areas are not efficient due
to the likely loss of attention. On the other side, unattended
surveillance systems require that people ana- lyze hours of recordings
when they have to search for some specific events, e.g. identify
people responsible of violence, theft or other offences. In many cases
a specific search in the video has to be accomplished in the shortest
amount of time. This paper presents MotionFinder, a tool that performs
video analysis by computing an interactive summarization of the
movements in a scene. Once the summarization process is complete, the
tool responds in real time to inquires. For example, human
investigators may search for specific areas in the video that show
high levels of activity or where they know that something occurred
(e.g.: property damaged or stolen). The tool responds by showing only
the scenes in which some activity occurred for that specific area of
the video.

C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti.
Educational games on a large multitouch screen.
Proc. of International Conference on Distributed Multimedia Systems (
DMS 2011).
Florence, Italy, August 18-20, 2011, SKOKIE: Knowledge Systems
Institute, pp. 242-245, ISBN/ISSN: 1-891706-30-6
Abstract -
pdf -
proceedings
DMS 2011 (pdf ~25MB)
Understanding how technology, coupled with skillful
pedagogical solutions, can help to innovate and improve learning at
school is the main goal of the �Learning for All� (L4A) research
project. The combination of educational games and advanced technology
has the potentiality of arousing pupils� attention, also engaging
them in learning activities while having fun. This paper presents two
educational games available through a large multitouch displays
installed in the hall of a primary school. Such games aim at
stimulating pupils to exercise their knowledge about history and
geography. Field studies have been planned to study both educational
and social aspects about the interaction with such games.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, D.
Caivano, M. F. Costabile, R. Lanzilotti , A. Bruun, J. Stage.
Usability evaluation: a survey of software development organizations.
Proc. of International Conference on Software Engineering and Knowledge
Engineering (
SEKE 2011). Miami, FL, USA, July 7-9, 2011, SKOKIE:
Knowledge Systems Institute, pp. 282-287, ISBN/ISSN: 1-891706-29-2
Abstract -
SEKE proceedings
The importance of usability engineering in software
development is acknowledged by an increasing number of software
organizations. This paper reports from a survey of the practical
impact of usability engineering in software development organizations.
The survey was conducted in Southern Italy, replicating one conducted
in Northern Denmark three years earlier. The results show that the
number of organizations conducting some form of usability activities
is nearly the same, but there are important differences in the
understanding of usability. The key advantages emphasized by the
respondents are product quality, user satisfaction and competitiveness
in both surveys. The main problems emphasized are developer mindset,
resource demands and customer participation.
2010
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno, A. L. Simeone.
Analysis of the UCD process of a web-based
system.
Proc. of International Conference on Distributed Multimedia Systems (DMS
2010). Oak Brook, Illinois, USA, 14-16 October, 2010, SKOKIE, ILLINOIS:
Knowledge Systems Institute, pp. 180-185, ISBN/ISSN: 1-891706-28-4
P. Buono, A. L. Simeone.
Video abstraction and detection of anomalies by
tracking movements.
Proc. of Advanced Visual Interfaces (AVI 2010). Rome, Italy, May, 26-28,
2010, pp. 249-252, NEW YORK: ACM, ISBN/ISSN: 978-1-4503-0076-6.

C. Ardito, P.
Buono, M.F. Costabile, R. Lanzilotti.
Gameplay to support learning with new
technologies.
Next Generation of HCI and Education: Workshop on UI Technologies and
Educational Pedagogy, CHI 2010 International Conference, Atlanta, GA,
USA, April 10-15 2010.
P. Buono, A. L. Simeone.
An Experience about User Involvement for
Successful Design
In: Information Systems: People, Organizations, Institutions and
Technologies, A. D'Atri and D. Saccà (Eds.), Business and Economics,
Part 9, Physica-Verlag HD, Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 503-510, 2010. ISBN
978-3-7908-2147-5.
2009
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, A. L. Simeone.
An information visualization approach to
hospital shifts scheduling.
In: J.A. Jacko ed. Human-Computer Interaction, Part IV. vol. LNCS 5613,
pp. 439-447, 2009, Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag (Germany), ISBN:
978-3-642-02582-2.
M. Brattoli, P. Buono, M.
Caselli, L. D'Accolti, G. De Gennaro, A. Loiotile Demarinis, M. Musti,
M. Tutino.
Voc and odor: valutazione delle emissioni di
composti organici volatili e degli impatti odorigeni prodotti dai
nuovi materiali e dalle nuove tecnologie per i sistemi produttivi
(2009).
Environmental Including Global Change, Palermo, 5-9 ottobre 2009.
P. Buono,
P. Di Bitonto, F. Di Tria, V. L. Plantamura.
Genómena: a Knowledge-Based System for the
Valorization of Intangible Cultural Heritage.
Proc. DMS 2009. San Francisco, CA, USA, September 10-12, 2009.
Knowledge Systems Institute Graduate School (UNITED STATES), pp.
100-105, ISBN/ISSN: 1-891706-25-X.
P. Buono,
A.L. Simeone, C. Ardito, M.F. Costabile and R. Lanzilotti.
Visualizing data to support tracking in food
supply chain.
Proc. DMS 2009, San Francisco, CA, USA, September 10-12, 2009,
Knowledge Systems Institute Graduate School (UNITED STATES), pp.
369-374, ISBN/ISSN: 1-891706-25-X.
M. Brattoli, P. Buono, M.
Caselli, L. D'Accolti, G. De Gennaro, M. Musti, M. Tutino.
VOC and ODOR: Evaluation of the volatile
organic compounds emissions and of the olfactory impacts produced by
new materials and by new technologies for productive system.
XXIII Congresso Nazionale della Società Chimica Italiana, Sorrento 5-10
Luglio 2009.
C. Ardito, P.
Buono, M.F. Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno and A.L.
Simeone.
Exploring Archaeological Parks by Playing
Games on Mobile Devices.
In: CHItaly 2009. Rome, Italy, June 17-19, 2009, pp. 81-85, ISBN/ISSN:
978-88-88044-14-9
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno.
Enabling interactive exploration of cultural
heritage: an experience of designing systems for mobile devices.
Knowledge Technology and Policy, 22(1), 2009, pp. 79-86.
doi:10.1007/s12130-009-9079-7.
Abstract -
pdf
Interaction design of mobile systems is a complex
activity because it requires to consider new usability and user
experience aspects in order to exploit the peculiar characteristics of
mobile devices, such as their pervasive and ubiquitous nature. This
paper discusses issues about designing, developing and evaluating
mobile systems. Italy has a rich cultural heritage and the focus here
is on the design of systems that enable interactive exploration of
historical sites, not only for enhancing the user experience but also
for learning purposes. It is reported the experience of researchers of
the Interaction, Visualization and Usability lab at the University of
Bari, Italy, in designing a mobile learning system, called Explore!,
that supports young students learning ancient history during a visit
to archaeological parks. The evaluation of Explore! through systematic
field studies shows that the adopted approach is able to transform the
visit to archaeological parks into a more complete and culturally rich
experience.

C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti and A. L. Simeone.
Comparing low cost input devices for
interacting with 3D Virtual Environments
Proc. HSI'09, Catania, Italy, May 21-23, 2009, pp. 292-297, ISBN:
978-1-4244-3960-7.
Abstract -
pdf
-
Ieee
Xplore
Interaction with 3D Virtual Environments has always
suffered from a lack of widely available and low cost input devices.
Recently, thanks to the diffusion of gaming systems such as the
Microsoft XBox 360 or the Nintendo Wii, new input devices are on the
market at a relatively cheap price. This paper describes a study whose
aim is to compare input devices in order to identify effective
alternatives for the mouse and keyboard in such settings where their
use is not advisable or feasible, e.g. museums and other public areas.
This study has been carried out using a 3D Virtual Environment in
which the participants were required to perform three canonical 3D
interaction tasks. Two different groups participated to the test: the
first group was involved in a pilot study to check the test
environment. The second group performed the test.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno.
A tool for Wizard of Oz studies of multimodal
mobile systems.
Proc. HSI'09, Catania, Italy, May 21-23, 2009, pp. 344-347, ISBN:
978-1-4244-3960-7.
Received the
Best Paper Award in the area of
Human-centered Computing System Design.
Abstract -
pdf
The MuMoWOz (MultiModal Wizard of Oz) tool presented in
this paper permits to conduct Wizard of Oz user studies. The
significant features of MuMoWOz are the possibility to easily adapt it
to new simulation scenarios and an architecture that allows HCI
researchers to perform studies in mobile multimodal settings. The
simulation of two scenarios related to cultural heritage domain is
reported.
2008

C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, T. Pederson, A. Piccinno.
Experiencing the Past through the Senses: An
M-Learning Game at Archaeological Parks.
IEEE MultiMedia, vol. 15, no. 4, Oct-Dec, 2008, pp. 76-81, ISSN
1070-986X.
Abstract -
pdf
The use of computers in education has escalated rapidly
during the last two decades. At the same time, technology advances
have opened a new field of use, namely computer-based edutainment
education in the form of entertainment where learners can achieve
their learning goals while having fun. By meeting some of their
psychological needs, computer games, if adequately designed, can
motivate children to learn. Research on this approach has paved the
way for the use of electronic games not only for pure entertainment
but also as education tools.
The deployment of location-based multimedia services is continuously
expanding from its early use in tourist guide systems and art
installations to current, widespread applications such as vehicle
navigation assistance and mobile gaming. Games on mobile phones, more
than other interactive technologies, have become a significant part of
the contemporary culture experienced by young people. Mobile games
that associate real-world elements with the virtual objects on the
phone, as occurs in augmented reality and context-aware systems, open
up a wider game design space by exploiting multimedia and multimodal
features of real-world elements. A representative example on how
ubiquitous and mobile technologies can provide opportunities for novel
learning experiences out of the classroom is discussed elsewhere.
The use of mobile games as learning tools is gaining increased support
for several reasons: mobile devices are associated with low cost,
accessibility, flexibility, and portability. Furthermore, mobile games
are engaging, and inspire curiosity and increased motivation. In
addition, mobile games as educational media are supported by
pedagogical theories, including constructivism, in which learners
actively construct their own knowledge instead of passively receiving
information from a teacher or guide, and situated cognition, in which
students draw on real-world situations and become immersed in
particular circumstances. Empirical studies have shown evidence that
educational electronic games promote effective learning, primarily of
mathematics, science, physics, music, game accessibility guidelines,
and history.
M-learning games, such as the one presented in the main article, imbue
young students with a better understanding of history, helping players
to acquire deeper knowledge while playing in an archaeological park.
The gameplay method offers several benefits. Firstly, play is fun and
amusing. Because it's enjoyably, players are less likely to forget
learned facts and skills; hence, this property of the gameplay method
brings obvious pedagogical benefits. A second positive aspect of play
is that different skills can be practiced simultaneously. In a
group-based game like Explore!, each player contributes with her or
his most congenial skills. Finally, play is a relational activity,
stimulating collaboration and encouraging interaction within and among
groups.
A. L. Simeone,
P. Buono.
Evacuation Traces Mini Challenge: User Testing
to Obtain Consensus - Discovering the Terrorist.
Proc. of IEEE Symposium on VAST 2008, October 21-23, 2008, Columbus,
Ohio USA, pp. 209-210, D. Ebert and T. Ertl (Eds.) IEEE Computer Society
Press, ISBN: 978-1-4244-2935-6.
Received the
Evacuation Traces Mini Challenge
Award: User Testing to Obtain Consensus Answers
www
P. Buono, T. Cortese, F.
Lionetti, M. Minoia, A. L. Simeone.
A Simulation of a Fire Accident in Second Life.
Proc. of the 11th Conference on Presence, October 16-18, 2008, Padova,
Italy, pp. 183-190, A. Spagnoli and L. Gamberini (Eds.), ISBN
978-88-6129-287-1.
Abstract -
pdf
Simulating the evacuation of an office building can be
helpful to better prepare the potential occupants in the event of
fire. Virtual environments are the ideal candidates for this type of
simulations because they allow testing of numerous scenarios with
minimal costs. We also needed a multiplayer collaborative environment
for our experiment and for this reason, our choice fell on Second
Life. In our study numerous tests were conducted on various groups of
users to analyze their behavior and reactions and experienced through
a virtual environment during a dangerous situation. In this paper we
describe how our experiment was enacted and the results and
observations made after the tests.
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, A. De Angeli, R. Lanzilotti.
Combining Quantitative and Qualitative Data for
Measuring User Experience of an Educational Game.
Proceedings of the International Workshop on Meaningful Measures: Valid
Useful User Experience Measurement (VUUM) Reykjavik, Iceland, June 18th
2008, pp. 27-31. ISBN: 978-2-917490-02-0
C. Ardito, P. Buono, R.
Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno, M. Corallo, V. Sepe.
Il Gioco-Escursione: una Tecnica di
Apprendimento per Sistemi di m-Learning.
Proc. of DIDAMATICA 2008, Taranto, Italy. ISBN: 978-88-902981-2-7.

M. F. Costabile, A. De Angeli, R. Lanzilotti,
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, T. Pederson.
Explore! Possibilities and Challenges of Mobile
Learning.
Proc. of Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems 2008 (CHI
2008). Florence, Italy. APRIL 5-10, 2008. New York: ACM Press.
Abstract -
pdf
-

This paper reports the experimental studies we have
performed to evaluate Explore!, an m-learning system that supports
middle school students during a visit to an archaeological park. It
exploits a learning technique called excursion-game, whose aim is to
help students to acquire historical notions while playing and to make
archaeological visits more effective and exciting. In order to
understand the potentials and limitations of Explore!, our studies
compare the experience of playing the excursion-game with and without
technological support. The design and evaluation of Explore! have
provided knowledge on the advantages and pitfalls of m-learning that
may be instrumental in informing the current debate on e-learning.
P. Buono, A. L. Simeone.
Interactive Shape Specification for Pattern
Search in Time Series.
In: Proc. AVI 2008. Napoli, 28-30 Maggio 2008, NEW YORK: ACM, pp.
480-481, ISBN/ISSN: 0-978-60558-141-5

2007
C. Ardito,
P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, T. Pederson.
Re-experiencing History in Archaeological Parks
by Playing a Mobile Augmented Reality Game.
In: R. Meersman, Z. Tari, P. Herrero et al. (Eds.), (vol. LNCS 4805, pp.
357-366). BERLIN: Springer (GERMANY).
Abstract -
pdf
-
Springer
This paper presents a mobile system that supports young
students learning history at an archaeological site. It adopts
gameplay as a novel and effective technique particularly suited for
learning through mobile systems (m-learning). From a technological
point of view, the main novelty of our system is its slim
architecture. Minimal investments are required because the system runs
on the students� own cellular phones. Experimental studies indicate
that gameplay is able to trigger a desire to learn more about ancient
history and to make archaeological visits more exciting and learning
about the past more effective.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono , M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, T. Pederson.
Mobile games to foster the learning of history
at archaeological sites.
Proc. of IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages and Human-Centric Computing
(VL/HCC 2007), Coeur d’Alène, Idaho, Usa, September 23-27, 2007, (pp.
81-84).
Abstract -
pdf
This paper presents a system designed to support young
students learning history at an archaeological site, by exploiting
mobile technology. The approach uses game-play, since it stimulates in
young students an understanding of history that would otherwise be
difficult to engender, helping players to acquire historical notions
and making archaeological visits more effective and exciting. A
strength of the system is that, by running on the visitors own
cellular phones, it requires minimal investments and small changes to
the existing site exhibition.
P. Buono, C. Plaisant, A.
Simeone, A. Aris, B. Shneiderman, G. Shmueli, W. Jank.
Similarity-Based Forecasting with Simultaneous
Previews: A River Plot Interface for Time Series Forecasting.
Proc. of 11th International Conference Information Visualization (IV
'07), 2007, pp. 191-196.
Abstract -
pdf
-
ACM -
IEEEXplore
Time-series forecasting has a large number of
applications. Users with a partial time series for auctions, new stock
offerings, or industrial processes desire estimates of the future
behavior. We present a data driven forecasting method and interface
called Similarity-Based Forecasting (SBF). A pattern matching search
in an historical time series dataset produces a subset of curves
similar to the partial time series. The forecast is displayed
graphically as a river plot showing statistical information about the
SBF subset. A forecasting preview interface allows users to
interactively explore alternative pattern matching parameters and see
multiple forecasts simultaneously. User testing with 8 users
demonstrated advantages and led to improvements.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile.
A Visualization tool for Multidimensional data
analysis.
XV Convegno Nazionale su Sistemi Evoluti per Basi di Dati (SEBD), June
17-20, 2007, Torre Canne di Fasano (Brindisi), Italy.
P. Buono.
Simultaneous Previews for Time Series
Forecasting.
XV Convegno Nazionale su Sistemi Evoluti per Basi di Dati (SEBD), June
17-20, 2007, Torre Canne di Fasano (Brindisi), Italy.
P. Buono.
Time Series: a forecasting preview interface.
Proc. of CHItaly, June 28-30, 2007, Padova, Italy.
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile, R. Lanzilotti, T. Pederson.
Can Mobile Games Make Learning History at
Archaeological Parks Fun and Instructive?
Proc. of CHItaly, June 28-30, 2007, Padova, Italy.
2006
C. Ardito,
P. Buono,
Costabile M., R. Lanzilotti (2006).
Two Different Interfaces to Visualize Patient
Histories on a PDA.
Proc. of MobileHCI '06, Espoo, Finland. September 12-15, 2006. (pp.
37-40). New York: ACM Press (United States). ISBN/ISSN: 1-59593-390-5.
Abstract -
pdf
-

PHiP (Patient History in Pocket) is a tool designed for
a mobile device that displays patient histories and permits to
visually query patient data stored in the hospital database. It
exploits Information Visualization techniques and it is able to
accommodate on the screen a good amount of information that physicians
require in their analysis of clinical cases. Two different user
interfaces for PHiP have been implemented and informal user testing
has been performed to compare their impact on users.
P. Buono, C. Ardito, Costabile
M., R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno.
DAE: a Visualization-based System for Data
Analysis.
Proc. of Visual Languages and Human-Centric Computing 2006 (VL/HCC
2006), Brighton, United Kingdom, September, 4-8, 2006, pp. 147-150.
C. Ardito,
P. Buono,
Costabile M., R. Lanzilotti.
Systematic inspection of information
visualization systems.
Proc. of the 2006 conference on BEyond time and errors: novel evaluation
methods for information visualization, Venice, Italy, 2006, SESSION:
Methodologies: heuristics for information visualization Pages: 1 - 4,
ISBN:1-59593-562-2,
http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1168149.1168163.
-

C. Ardito, R. Lanzilotti,
P. Buono,
A. Piccinno.
A Tool to Support Usability Inspection.
Proc. of AVI 06, Venice, Italy, May 23-26, 2006, pp. 278-281. -

2005
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile.
Visualizing Patient Histories on Mobile
Devices.
Proc. of AICA 2005, Udine, Italy, October 5-7, pp. 579-586.
C. Ardito, P. Buono, M. F.
Costabile.
The Challenge of Visualizing Patient Histories
on a Mobile Device.
In: M.F. Costabile M., F. Paterno' Human-Computer Interaction - INTERACT
2005. (vol. LNCS 3585, pp. 942-945). ISBN: 3-540-28943-7. Berlin:
Springer (Germany).
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile.
How visualization may help in understanding
association rules.
Proc. of HCItaly 2005, Rome, Italy, September 13, pp. 100-104.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, E.
Covino, G. Pani.
A visual tool for multidimensional data
analysis.
Proc. of International Workshop on Visual Languages and Computing 2005,
Banff, Canada, September 5-7, 2005, pp. 333-338.
A. Appice , P. Buono.
Analyzing multi-level spatial association rules
through a graph-based visualization.
In: F. Esposito (eds.), "IEA/AIE 2005" (vol. LNCS 3533, pp. 448-458),
ISBN 978-3-540-26551-1, Berlin: Springer (Germany), 2005.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile.
Visualizing Association Rules in a Framework
for Visual Data Mining.
In: M. Hemmje et al (eds.), 'From Integrated Publication and
Informations Systems to Virtual Information and Knowledge Environments',
(vol. LNCS 3379, pp. 221-231), ISBN 3-540-24551-0, Berlin: Springer
(Germany), 2005.
P. Buono, A. Aris, C. Plaisant, A.
Khella, B. Shneiderman.
Interactive Pattern Search in Time Series.
Visualization and Data Analysis, VDA 2005, 16-20 January 2005,
San Jose, CA USA, SPIE, Washington DC, 175-186.
2004
P. Buono.
Visual Data Analysis: the case of Trade Fairs.
AICA 2004, 28-30 September, Benevento, Italy, pp. 733-743.
D. Bruzzese,
P. Buono.
Combining Visual Techniques for Association
Rules Exploration.
AVI 2004, 25-28 May, Gallipoli, Italy, pp. 381-384. -

2003
P. Buono.
Analysing Association Rules with an Interactive
Graph-Based Technique.
Special Session on Visual Data Mining, HCI International 2003,
22-27 June, Crete, Greece, pp. 675-679.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, S. P. Guida,
R. Lanzilotti, A. Piccinno.
Improving Web Interaction through
Personalization.
HCI International 2003, Crete, Greece, June 22-27, 2003, pp.
522-526.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, D. Grilli, S.
P. Guida, P. Lops, G. Semeraro.
Integrating machine learning and filtering
techniques to improve recommendations.
CHI '03 Workshop on Designing Personalized User Experiences for
eCommerce: Theory, Methods, and Research, Fort Lauderdale, USA,
6-7 April 2003
2002
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, M. Hemmje, G.
Jäschke.
Analysing Data Through Visualizations in a
Web-based Trade Fair System.
The fourteenth International Conference on Software Engineering and
Knowledge Engineering, Ischia, Italy, July 15-19, 2002, ACM
Press, pp. 579-582.

P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, S. Guida, A.
Piccinno.
Integrating User Data and Collaborative
Filtering in a Web Recommendation System.
In 'Hypermedia: Openness, Structural Awareness, and Adaptivity', Reich,
S., Tzagarakis, M.M., and De Bra, P.M.E. (Eds.), Springer Lecture Notes
on Computer Science, Vol. 2266, February 2002.
2001
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, F. A. Lisi.
Supporting Data Analysis Through
Visualizations.
Proc. Workshop on Visual Data Mining, Freiburg, Germany, 4
September 2001, pp. 67-78.
E. Pauselli, A. D'Atri, P. Buono, M.F.
Costabile, M. Hemmje, G. Jäschke, C. Muscogiuri.
FAIRWIS Usage for Virtual Learning in Student
Micro Enterprises.
Proc. ED-MEDIA 2001, Tampere, Finland, June 25-30, pp.
1465-1467.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, S. Guida, A.
Piccinno, G. Tesoro.
Integrating User Data and Collaborative
Filtering in a Web Recommendation System.
UM2001, Proc. Third Workshop on Adaptive Hypertext and Hypermedia
- Sonthofen, Germany, July 2001, pp. 129-140.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, M. Hemmje, G.
Jäschke, C. Muscogiuri.
Providing On-line Trade Fair Services with
FAIRWIS.
Proc. OESSEO 2001, Rome, 14-15 September 2001, pp.
147-152.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, A. Piccinno,
G. Minardi.
UPE: The FAIRWIS Personalisation Component.
Proc. OESSEO 2001, Rome, 14-15 September 2001, pp.
153-154.
F. Barbini, P. Buono, M. F. Costabile,
A. D'Atri, E. Pauselli, S. Swift, Y. Ursa.
Requirement Analysis for On-line Trade Fairs.
Proc. OESSEO 2001, Rome, September 14-15 2001, 142-146.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, A. D'Atri, M.
Hemmje, G. Jäschke, C. Muscogiuri, E. Pauselli, F. Barbini.
FAIRWIS: A System for Improving On-line Trade
Fair Services.
Proc. E-work and E-commerce E2001, Venice, Italy, October 17-19,
2001, pp. 519-525.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, A. Piccinno,
T. Roselli.
Web Recommendation Systems: The Case of On-line
Trade Fairs.
Proc. PC-HCI 2001, Patras, Greece, December 7-9, 405-406.
P. Buono, M. F. Costabile, M. Di Fonzo.
Tecniche di Visualizzazione a Supporto
dell'Analisi dei dati in FAIRWIS.
Atti del VII Congresso Nazionale SIE, 26-28 September 2001,
Firenze, Italy, pp. 417-422.
Top of this page
Projects
Some projects he is, or was involved:
European projects
-
-
IST-2001-34290 FairsNet (On-line Solutions for Trade
Fairs), 2002-2003.
-
IST-1999-12641 FAIRWIS (Trade Fair Web-based Information
Services), 2000-2001.
-
BRRT-CT98-5089
RUCADI (Recovery
and Utilisation of CArbon Dioxide), 1999-2000.
National/regional projects
- Italian MISE (PON) VINCENTE: A Virtual collective INtelligenCe
ENvironment to develop sustainable Technology Entrepreneurship
ecosystems, 2013-2015.
- Italian MIUR (PON) LOGIN: LOGistica INtegrata - Industria 2015 -
Bando nuove tecnologie per il Made in Italy, 2012-2015.
- VOC and ODOR: valutazione delle emissioni di composti organici
volatili e degli impatti odorigeni prodotti dai nuovi impianti e dalle
nuove tecnologie per i sistemi produttivi, 2009-2011
- DIPIS (DIstributed Production as Innovative System), 2007-2009.
- Genòmena (Beni Culturali Immateriali per la Ricostruzione della
Memoria Storica del Territorio), 2007-2008.
- MONICA - (MONItoraggio e Controllo Adattivo - mobilità merci
pericolose), 2007-2008
- CHAT (Cultural Heritage fruition & e-learning applications
Advanced(MultiModal) Technologies), 2006-2008.
- GeCo (Sistema di gestione della conoscenza per la competitività
dell'industria automotive), 2006-2007.
- Convenzione tra Regione Puglia (Assessorato all’Ambiente), ARPA
Puglia, Università degli Studi di Bari (Centro METEA), Università
degli Studi di Lecce (Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell'Innovazione,
Dipartimento di Fisica), CNR-ISAC a valere sulle linee 6a e 7a del
Programma Triennale per la Tutela dell’Ambiente della Regione Puglia
2005-2007.
- Ex MURST 60% 2010: “Tecnologie informatiche a supporto della
fruizione di beni culturali”
- Ex MURST 60% 2008: “Metodi di Visual Analytics per l'analisi di
informazioni eterogenee”
- Ex MURST 60% 2005: “Analisi di dati con tecniche visuali”
- Ex MURST 60% 2004: “Tecniche di Visualizzazione a supporto
dell'analisi dei dati”
- Ex MURST 60% 2003: “Tecniche di visualizzazione a supporto della
navigazione e della presentazione di dati su Web”
- P.O.P. Regione Puglia, "Monitoraggio della Qualità dell'Aria",
Misura 7.3.7, 1999-2001.
Top of this page
Teaching inside the University of
Bari
The website of courses listed below is available at the link http://www.di.uniba.it/~buono/
| |
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
| Intelligent Computing Systems |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Databases + Laboratory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Laboratory of Algorithms and Data
Structures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Design of the User Interaction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Informatics Laboratory I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Informatics Laboratory II |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Informatics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Laboratory of Databases +
Laboratory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Human-Computer Interaction
Laboratory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Spreadsheet management |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Laboratory and lectures for the Spreadsheet
management course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Lectures for the Human-Computer
Interaction course |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 2018/2019 - Security
in mobile environments, Laurea Magistrale (Master) in
Informatics Security
- 2018/2019 - Information
Visualization, Laurea Magistrale (Master) in Computer
Science Curriculum
- 2015-2019 - Software Development for Mobile devices,
Computer Science and Software Production Technologies Curriculum
- 2014/2015 - Software Development for Smartphones,
Computer Science and Software Production Technologies Curriculum
- 2014 - Intelligent Computing Systems,
Computer Science Curriculum
- 2002-2013 - Databases, Computer Science
Curriculum
- 2002-2013 - Laboratory of Algorithms and Data
Structures, Computer Science Curriculum
- 2007-2010 - Design of the User Interaction,
Computer Science and Software Production Technologies Curriculum
- 2008-2009 - Informatics Laboratory I,
Cultural Activities, Design and Management Curriculum
- 2008-2009 - Informatics Laboratory II,
Cultural Activities, Design and Management Curriculum
- 2007 - Informatics, History,
Science and Techniques of the Cultural Industry Curriculum
- 2002-2007 - Laboratory of Databases,
Computer Science and Digital Communication Curriculum
- 2006 - Human-Computer Interaction
Laboratory, SSIS Curriculum
- 2006-2007 - Spreadsheet management,
SSIS Curriculum
- 2006 - Laboratory and lectures for the Spreadsheet
management course, SSIS Curriculum
- 1999-2005 - Lectures for the Human-Computer
Interaction course, Computer Science Curriculum
Top of this page
Invited talks, seminars and other teaching activities
- 2018 - Invited Seminar organized by the Big Data
Forum at the Alliance Manchester Business School, The University of
Manchester (UK) - Information Visualization and Visual Analytics @
IVULab
- 2017 - Invited Talk at the Forum Media Technology
& All Around Audio Symposium - Capstone: Pervasive
Technologies to Enrich People Experience in Visiting Cultural
Heritage sites
- 2016 - Invited Talk at the Mathematics Department -
University of Bari Aldo Moro - Introduction to Information
Visualization (in Italian) - among the Colloqui
Matematici seminar cycles
- 2012 - Invited Talk at the Mobile Dev Camp Event (in Italian) about
prototyping. Pdf
slides are available (about 30 MB).
- 2011 - asp.net and C# lessons at the FIxO program:
"Formazione & Innovazione per l'Occupazione"
- 2003 - Human-Computer Interaction, Master on
"Distance Learning Designer"
- 2000 - Tutor at the SISS Puglia Course for teachers
on: "Multimedia Technologies, Internet and Office Automation"
- 2000 - Lectures on Visual Basic at "Centro
Interdipartimentale di Logica e Applicazioni" (CILA) inside the
INNOVAMEDIA project.
- 2000 - Course on Tools for Design and Developing
Multimedia on the Web inside the "MAHLER, Music And Hi-fi Lab.
Enterprise for Research" project, at the Music School of Bari.
Top of this page
Software
This is a very short list of software. For further and updated
information, please, contact Paolo Buono
- PAOHvis
- Analyzing Dynamic Hypergraphs with Parallel Aggregated Ordered
Hypergraph Visualization
- ClockBoxPlot, a tool for visualizing data using a clock metaphor
- CET (Catasto Emissioni
Territoriale per la Regione Puglia), is a system for the collection of
data related to industries of the Apulia region and their emissions in
the air
- TimeSearcher 2 and 3, Interactive tool for the multivariate time
series visualization with the possibility to search for interesting
patterns (implemented in C#); the official website is available at the
TimeSearcher
homepage
- DAE (Data Analysis Engine) is a framework for data analysis. It is
composed by different components
- DaeVET, Tool for database visualization and interaction
(implemented in Java)
- PCAR, Interactive tool for Association Rules Visualization
exploiting Parallel Coordinates technique (implemented in Java)
- ARVis, Interactive tool for Association Rules Visualization
exploiting a Graph-Based technique (implemented in Java)
- DaeTL, Interactive tool exploiting Table Lenses technique
(implemented in Java)
- DaeQP, Interactive tool exploiting Query Preview technique
(implemented in Java)
- SMARP, A system to support Air Quality Monitoring (implemented in
Visual Basic 6)
Further information about software can be accessed at the tools
webpage. Please, consider that it is still an under construction
page.
Top of this page


![]() allow
visitors who click on it to obtain the definitive version of the article
from the ACM Digital Library at no charge. Please make sure that the
address of this page visualized in your browser is: http://ivu.di.uniba.it/people/buono.htm
allow
visitors who click on it to obtain the definitive version of the article
from the ACM Digital Library at no charge. Please make sure that the
address of this page visualized in your browser is: http://ivu.di.uniba.it/people/buono.htm